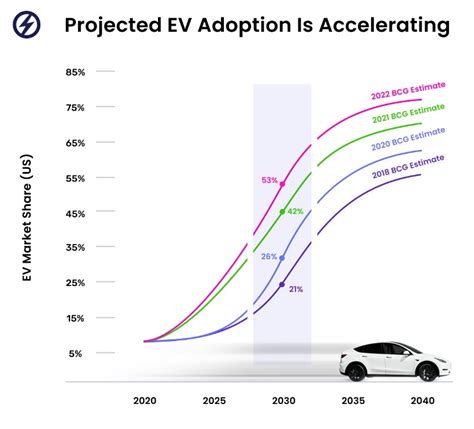
Electric vehicle demand is soaring, but consumer anxiety over limited range and charging infrastructure remains a significant hurdle to wider EV adoption, according to a recent BMW-sponsored study. The research highlights a critical juncture for the automotive industry as it navigates the transition to electric mobility.
A comprehensive study commissioned by BMW reveals a paradox in the electric vehicle market: while consumer interest in EVs is undeniably increasing, persistent concerns about range anxiety and the availability of convenient charging options are acting as major deterrents for potential buyers. The study, which delved into consumer perceptions and attitudes towards electric vehicles, underscores the challenges facing automakers and policymakers as they strive to accelerate the adoption of electric mobility.
The BMW study, which surveyed a representative sample of consumers, found that a significant proportion of respondents expressed strong interest in owning an EV in the future. This enthusiasm is driven by a number of factors, including growing awareness of the environmental benefits of electric vehicles, the rising cost of gasoline, and the increasing availability of compelling EV models from various manufacturers. However, the study also revealed that these positive sentiments are often overshadowed by anxieties related to range and charging.
Range anxiety, the fear of running out of battery power before reaching a charging station, remains a primary concern for many potential EV buyers. Consumers worry about the limitations of current EV range, particularly on long trips or in areas with limited charging infrastructure. “The study highlights that even with increasing range capabilities in new EV models, consumers still perceive range as a significant barrier,” said a BMW spokesperson familiar with the study’s findings. “This perception often stems from a lack of real-world experience with EVs and a reliance on anecdotal information.”
In addition to range anxiety, the availability and reliability of charging infrastructure are also major concerns. Many consumers are unsure about where they can charge their EVs, how long it will take to charge, and how much it will cost. The lack of a widespread and convenient charging network, particularly in rural areas and apartment complexes, is hindering EV adoption. Furthermore, concerns about the reliability of existing charging stations, including issues with availability and functionality, are adding to consumer anxiety.
The BMW study emphasizes the need for a multi-pronged approach to address these challenges. Automakers, governments, and charging infrastructure providers must work together to increase the availability of public charging stations, improve the reliability of charging infrastructure, and educate consumers about the benefits and realities of EV ownership.
Addressing Range Anxiety
One of the key strategies for overcoming range anxiety is to continue to improve the range capabilities of electric vehicles. Automakers are investing heavily in battery technology to increase energy density and extend the driving range of their EVs. New EV models are now capable of traveling over 300 miles on a single charge, and this number is expected to increase in the coming years.
However, simply increasing range is not enough. Consumers also need accurate and reliable information about the real-world range of EVs. Automakers should provide clear and transparent range estimates, taking into account factors such as driving conditions, temperature, and payload. Furthermore, navigation systems should be integrated with real-time charging station information, allowing drivers to easily locate and navigate to available charging stations along their route.
Consumer education is also crucial. Many consumers overestimate the frequency with which they would need to charge an EV. By providing realistic information about driving habits and charging needs, automakers can help alleviate range anxiety and encourage potential buyers to consider EVs.
Expanding Charging Infrastructure
The expansion of charging infrastructure is essential for the widespread adoption of electric vehicles. Governments and private companies are investing billions of dollars in building out a national charging network. The goal is to provide convenient and reliable charging options for EV drivers, whether they are at home, at work, or on the road.
The charging network must include a mix of charging speeds, from Level 2 chargers that can add 20-30 miles of range per hour to DC fast chargers that can provide a significant charge in as little as 30 minutes. DC fast chargers are particularly important for long-distance travel, allowing EV drivers to quickly replenish their batteries and continue their journey.
In addition to expanding the physical infrastructure, it is also important to improve the reliability and accessibility of charging stations. Charging stations should be well-maintained and easy to use. Payment systems should be standardized, and drivers should be able to easily locate and access charging stations through mobile apps and navigation systems.
Government Incentives and Policies
Government incentives and policies can play a significant role in accelerating the adoption of electric vehicles. Tax credits, rebates, and other financial incentives can help reduce the upfront cost of EVs, making them more affordable for consumers. Governments can also provide funding for the development of charging infrastructure and support research into advanced battery technology.
Furthermore, governments can implement policies that encourage the use of electric vehicles, such as preferential parking for EVs, access to HOV lanes, and exemptions from congestion charges. These policies can help make EVs more attractive to consumers and encourage them to switch from gasoline-powered vehicles.
The Future of Electric Mobility
The BMW study highlights the challenges and opportunities facing the electric vehicle market. While consumer interest in EVs is growing, range anxiety and charging infrastructure concerns remain significant barriers to wider adoption. By addressing these challenges through technological innovation, infrastructure investment, and consumer education, automakers and policymakers can pave the way for a future of electric mobility.
The transition to electric vehicles is not just about reducing emissions and protecting the environment. It is also about creating new jobs, fostering innovation, and enhancing energy security. Electric vehicles are more energy-efficient than gasoline-powered vehicles, and they can be powered by renewable energy sources such as solar and wind. By embracing electric mobility, we can create a cleaner, more sustainable, and more prosperous future.
The study serves as a reminder that while technological advancements are crucial, understanding and addressing consumer anxieties are equally important for fostering widespread EV adoption. BMW’s investment in this research underscores the company’s commitment to not only producing innovative electric vehicles but also contributing to the broader understanding of the challenges and opportunities within the evolving EV landscape.
Digging Deeper: Factors Influencing EV Adoption
Beyond range and charging, several other factors influence consumer decisions regarding EV adoption. These include purchase price, vehicle performance, availability of different models, and overall cost of ownership.
Purchase Price: The upfront cost of an EV is often higher than that of a comparable gasoline-powered vehicle. This price difference can be a significant barrier for many consumers, particularly those on a tight budget. However, government incentives and tax credits can help reduce the upfront cost of EVs, making them more affordable.
Vehicle Performance: Electric vehicles offer instant torque and smooth acceleration, making them fun to drive. However, some consumers may be concerned about the performance of EVs in certain conditions, such as cold weather or when towing heavy loads. Automakers are continuously working to improve the performance of EVs and address these concerns.
Availability of Different Models: The range of EV models available on the market is constantly expanding. Consumers now have a wide variety of choices, from compact cars to SUVs to trucks. However, some consumers may still find that there is not an EV model that perfectly meets their needs.
Overall Cost of Ownership: While the upfront cost of an EV may be higher, the overall cost of ownership can be lower than that of a gasoline-powered vehicle. EVs typically have lower fuel costs and require less maintenance. Over the lifetime of the vehicle, these savings can add up and offset the higher purchase price.
The Role of Automakers
Automakers play a crucial role in accelerating the adoption of electric vehicles. They are responsible for developing and producing compelling EV models, improving battery technology, and educating consumers about the benefits of EV ownership.
Automakers are investing billions of dollars in electric vehicle development. They are developing new battery technologies that offer longer range, faster charging times, and lower costs. They are also designing EVs that are more stylish, more functional, and more fun to drive.
In addition to developing new EV models, automakers are also working to improve the charging experience. They are partnering with charging infrastructure providers to expand the charging network and make it easier for EV drivers to charge their vehicles. They are also developing mobile apps and navigation systems that provide real-time information about charging station locations and availability.
Furthermore, automakers are actively engaged in consumer education. They are providing information about the benefits of EV ownership, addressing common misconceptions about EVs, and offering test drives to potential buyers. They are also working with governments and other stakeholders to promote policies that support the adoption of electric vehicles.
The Impact of COVID-19
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a mixed impact on the electric vehicle market. On the one hand, the pandemic has disrupted supply chains and slowed down production, leading to shortages of EVs in some markets. On the other hand, the pandemic has also increased awareness of the environmental benefits of electric vehicles and accelerated the shift towards remote work, which can reduce the need for daily commuting.
As the world recovers from the pandemic, the electric vehicle market is expected to continue to grow rapidly. The demand for EVs is being driven by a number of factors, including growing environmental concerns, rising gasoline prices, and increasing government support for electric mobility.
The Competitive Landscape
The electric vehicle market is becoming increasingly competitive, with new players entering the market and established automakers ramping up their EV production. Tesla remains the dominant player in the EV market, but other automakers, such as BMW, General Motors, Ford, and Volkswagen, are making significant investments in electric vehicles and are poised to challenge Tesla’s dominance.
The increased competition is good for consumers, as it is driving innovation and lowering prices. Consumers now have a wider range of choices when it comes to electric vehicles, and they can expect to see even more options in the future.
The Importance of Collaboration
The transition to electric mobility is a complex undertaking that requires collaboration between automakers, governments, charging infrastructure providers, and other stakeholders. By working together, these stakeholders can overcome the challenges and accelerate the adoption of electric vehicles.
Automakers need to invest in the development of compelling EV models and improve battery technology. Governments need to provide incentives for EV purchases and support the development of charging infrastructure. Charging infrastructure providers need to expand the charging network and improve the reliability of charging stations. And consumers need to be educated about the benefits of EV ownership.
By working together, we can create a future of electric mobility that is cleaner, more sustainable, and more prosperous.
BMW’s Strategic Approach
BMW’s commitment to electric mobility extends beyond the findings of this study. The company is actively investing in the development of new electric vehicle models, battery technology, and charging infrastructure. BMW’s strategic approach includes:
- Expanding its EV portfolio: BMW plans to launch a range of new electric vehicles in the coming years, covering a variety of segments and price points.
- Investing in battery technology: BMW is investing heavily in research and development to improve the range, performance, and cost of batteries.
- Partnering with charging infrastructure providers: BMW is working with charging infrastructure providers to expand the charging network and make it easier for EV drivers to charge their vehicles.
- Providing customer support: BMW is providing comprehensive customer support to EV owners, including assistance with charging, maintenance, and troubleshooting.
- Promoting sustainable manufacturing: BMW is committed to sustainable manufacturing practices, reducing its environmental impact throughout the entire lifecycle of its vehicles.
BMW’s comprehensive approach to electric mobility reflects its commitment to a sustainable future and its belief that electric vehicles will play a central role in the automotive industry.
Beyond Personal Vehicles: The Electrification of Commercial Fleets
The electrification trend extends beyond personal vehicles, with a growing emphasis on electrifying commercial fleets. Businesses are increasingly recognizing the economic and environmental benefits of transitioning their fleets to electric vehicles. Electric commercial vehicles can significantly reduce fuel costs, lower maintenance expenses, and improve air quality in urban areas.
However, the electrification of commercial fleets also presents unique challenges. Commercial vehicles often have high mileage and require specialized charging infrastructure. Businesses need to carefully consider their charging needs and invest in the appropriate charging solutions.
Governments are providing incentives and support to encourage the electrification of commercial fleets. Tax credits, rebates, and other financial incentives can help businesses reduce the upfront cost of electric commercial vehicles. Governments are also providing funding for the development of charging infrastructure for commercial fleets.
The Global Perspective
The electric vehicle market is growing rapidly around the world, with different regions adopting EVs at different rates. China is currently the largest EV market in the world, followed by Europe and North America.
China’s government has been a strong supporter of electric vehicles, providing generous incentives and investing heavily in charging infrastructure. Europe is also seeing strong growth in EV sales, driven by stricter emissions regulations and growing consumer awareness of the environmental benefits of electric vehicles. North America is lagging behind China and Europe in terms of EV adoption, but the market is expected to grow rapidly in the coming years as more EV models become available and charging infrastructure expands.
The Long-Term Vision
The long-term vision for electric mobility is a future where electric vehicles are the dominant form of transportation. This vision requires a number of key developments, including:
- Continued improvements in battery technology: Battery technology needs to continue to improve in terms of range, performance, cost, and safety.
- Widespread availability of charging infrastructure: Charging infrastructure needs to be widely available and easy to use, both in urban and rural areas.
- Lower EV prices: EV prices need to come down to be competitive with gasoline-powered vehicles.
- Increased consumer awareness: Consumers need to be educated about the benefits of EV ownership and address common misconceptions about EVs.
- Supportive government policies: Governments need to continue to support the adoption of electric vehicles through incentives, regulations, and investments in infrastructure.
By working together, automakers, governments, charging infrastructure providers, and consumers can make this vision a reality and create a future of electric mobility that is cleaner, more sustainable, and more prosperous.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What are the main findings of the BMW study on EV demand?
A1: The BMW study reveals that while consumer interest in electric vehicles is increasing significantly, range anxiety and concerns about the availability and reliability of charging infrastructure remain major obstacles to widespread EV adoption. Consumers are enthusiastic about the environmental benefits and potential cost savings of EVs, but are hesitant due to the perceived limitations of current EV technology and infrastructure.
Q2: What is “range anxiety” and why is it a concern for potential EV buyers?
A2: “Range anxiety” is the fear that an electric vehicle’s battery will run out of power before the driver can reach a charging station. This concern stems from the limited range of some EVs and the lack of a widespread, reliable charging network, particularly in rural areas. The BMW study indicates that range anxiety is a significant deterrent for potential EV buyers, even with advancements in battery technology.
Q3: What steps are being taken to address the lack of charging infrastructure for EVs?
A3: To address the charging infrastructure gap, governments and private companies are investing heavily in expanding the charging network. This includes installing more public charging stations, increasing the availability of fast-charging options, and improving the reliability and accessibility of existing charging stations. Automakers are also partnering with charging providers to offer integrated charging solutions for EV owners.
Q4: What role do government incentives play in promoting EV adoption?
A4: Government incentives, such as tax credits, rebates, and subsidies, play a crucial role in making EVs more affordable and attractive to consumers. These incentives can help offset the higher upfront cost of EVs compared to gasoline-powered vehicles. Governments also support EV adoption through policies like preferential parking, HOV lane access, and funding for charging infrastructure development.
Q5: Beyond range and charging, what other factors influence consumer decisions about buying an EV?
A5: Besides range and charging, other key factors influencing EV adoption include the purchase price, vehicle performance, availability of different EV models, and the overall cost of ownership (including fuel and maintenance costs). Consumers also consider the environmental benefits of EVs, government incentives, and the availability of convenient charging options when making their purchasing decisions.