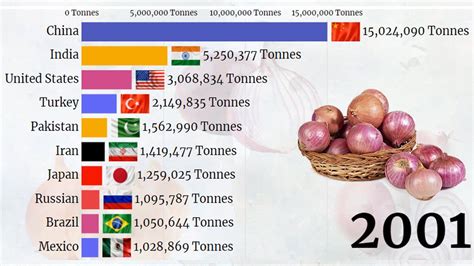
India has emerged as the world’s leading onion producer, surpassing China and solidifying its dominance in the global onion market, according to recent data. This surge in production underscores India’s agricultural prowess and its critical role in supplying this essential vegetable to countries worldwide.
India has officially claimed the title of the world’s top onion producer, outpacing its closest competitor, China. The rise to this position reflects significant advancements in agricultural practices, favorable climate conditions, and strategic government support aimed at boosting onion cultivation across the country. This achievement not only enhances India’s agricultural standing but also ensures a more stable supply of onions for both domestic consumption and international export.
The agriculture sector in India has witnessed substantial growth in recent years, particularly in the production of staple crops and vegetables. Onions, a fundamental ingredient in numerous cuisines, hold a significant place in Indian agriculture. The country’s diverse climate and fertile lands provide an ideal environment for onion cultivation, enabling farmers to produce high-quality yields. This increased production capacity has allowed India to not only meet its own domestic demand but also become a major exporter of onions, contributing significantly to its agricultural economy.
The journey to becoming the world’s leading onion producer has involved various factors. Improved farming techniques, including the use of better seeds, advanced irrigation systems, and modern pest control methods, have played a crucial role. Additionally, government initiatives aimed at supporting farmers through subsidies, training programs, and infrastructure development have further bolstered onion production. These combined efforts have resulted in a substantial increase in both the quantity and quality of onions produced, positioning India at the forefront of the global market.
India’s onion production is spread across several states, with Maharashtra being the largest producer, contributing a significant portion of the country’s total output. Other key onion-producing states include Madhya Pradesh, Karnataka, Gujarat, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, Haryana, Andhra Pradesh, and Tamil Nadu. Each of these states benefits from unique agro-climatic conditions that support onion cultivation, allowing for year-round production and ensuring a consistent supply to both domestic and international markets.
The economic impact of India’s dominance in onion production is considerable. The onion trade generates substantial revenue for the country, supporting millions of farmers and agricultural workers. Furthermore, the export of onions to various countries contributes significantly to India’s foreign exchange earnings. The stability of the onion market also has a direct impact on consumer prices, both domestically and internationally, making India a crucial player in the global food supply chain.
However, the onion market is not without its challenges. Price volatility, influenced by factors such as weather patterns, storage facilities, and market demand, can significantly impact farmers’ incomes and consumer prices. In years of surplus production, prices may fall sharply, leading to losses for farmers. Conversely, in times of scarcity, prices can soar, affecting consumers. To address these issues, the Indian government has implemented various measures, including price stabilization funds, buffer stock schemes, and export regulations, aimed at ensuring a more stable and predictable onion market.
India’s agricultural policies have played a pivotal role in its success as an onion producer. The government has focused on providing farmers with access to quality seeds, fertilizers, and irrigation facilities, as well as promoting the adoption of modern farming techniques. Subsidies on agricultural inputs and credit facilities have also helped to reduce the financial burden on farmers, encouraging them to invest in onion cultivation. Furthermore, infrastructure development, including cold storage facilities and transportation networks, has been crucial in minimizing post-harvest losses and ensuring that onions reach markets in good condition.
Looking ahead, India is poised to maintain its leadership position in the global onion market. The country’s vast agricultural resources, coupled with its commitment to improving farming practices and supporting farmers, provide a solid foundation for sustained growth. However, continued investment in research and development, particularly in areas such as disease-resistant varieties and improved storage technologies, will be essential to addressing future challenges and ensuring the long-term sustainability of the onion industry.
The impact of India’s onion production extends far beyond its borders. As a major exporter of onions, India plays a critical role in supplying this essential vegetable to countries across the globe. Its ability to maintain a consistent and reliable supply is crucial for food security in many regions, particularly in countries where onions are a staple ingredient in local cuisine. Furthermore, India’s dominance in the onion market has significant implications for international trade and economic relations, strengthening its position as a key player in the global agricultural landscape.
The journey to becoming the world’s leading onion producer has been a testament to India’s agricultural resilience and innovation. By overcoming challenges and leveraging its strengths, India has not only secured its position as the “Onion King” but also demonstrated its commitment to feeding both its own population and the world.
Detailed Analysis and Expanded Context
India’s agricultural sector has undergone a significant transformation in recent decades, driven by technological advancements, policy reforms, and increased investment. The country’s diverse agro-climatic zones, ranging from arid deserts to fertile plains, enable the cultivation of a wide variety of crops, making it one of the world’s leading agricultural producers. Within this diverse agricultural landscape, onions hold a special place, both as a staple food and as a valuable export commodity.
The cultivation of onions in India dates back centuries, with evidence suggesting that it was introduced to the region through trade routes. Over time, onions have become an integral part of Indian cuisine, used in a wide range of dishes, from simple curries to elaborate biryanis. The versatility of onions, combined with their nutritional value and relatively long shelf life, has made them an essential ingredient in households across the country.
The economic importance of onions in India cannot be overstated. The onion trade supports millions of farmers, agricultural laborers, and traders, particularly in states like Maharashtra, where onion cultivation is a major source of livelihood. The export of onions also contributes significantly to India’s foreign exchange earnings, making it a key component of the country’s agricultural exports.
India’s rise to becoming the world’s leading onion producer has been a gradual process, driven by a combination of factors. Improved farming techniques, such as the use of hybrid seeds, drip irrigation, and integrated pest management, have significantly increased yields. Government initiatives, including subsidies on fertilizers and electricity, as well as investments in irrigation infrastructure, have also played a crucial role.
The government’s focus on promoting sustainable agriculture practices has also contributed to the growth of the onion industry. Programs aimed at encouraging farmers to adopt water-efficient irrigation techniques, reduce the use of chemical fertilizers, and implement integrated pest management strategies have helped to improve the environmental sustainability of onion cultivation.
However, the onion market in India is not without its challenges. Price volatility is a major concern, with prices fluctuating widely depending on supply and demand. Factors such as weather patterns, storage facilities, and export regulations can all impact onion prices, creating uncertainty for both farmers and consumers.
To address the issue of price volatility, the Indian government has implemented various measures, including the creation of a price stabilization fund and the establishment of buffer stock schemes. The price stabilization fund is used to intervene in the market when prices fall below a certain threshold, providing farmers with a guaranteed price for their produce. The buffer stock scheme involves the procurement and storage of onions during periods of surplus production, which can then be released into the market when prices rise.
The government has also implemented export regulations to manage the supply of onions in the domestic market. Export restrictions, such as minimum export prices and export quotas, are sometimes imposed to ensure that domestic demand is met before onions are exported. However, these regulations can also have unintended consequences, such as reducing export earnings and discouraging farmers from investing in onion cultivation.
Looking ahead, India faces several challenges in maintaining its leadership position in the global onion market. Climate change is a major concern, with erratic rainfall patterns and increasing temperatures potentially impacting onion yields. The lack of adequate storage facilities is also a problem, leading to significant post-harvest losses.
To address these challenges, India needs to invest in research and development to develop climate-resilient onion varieties and improve storage technologies. The government also needs to promote the adoption of sustainable agriculture practices and strengthen its infrastructure for the storage and transportation of onions.
Despite these challenges, India remains well-positioned to maintain its dominance in the global onion market. The country’s vast agricultural resources, coupled with its growing economy and expanding middle class, provide a strong foundation for continued growth. By addressing the challenges and capitalizing on its strengths, India can ensure that it remains the “Onion King” for years to come.
State-Wise Production and Regional Variations
Maharashtra: Known as the “Onion Bowl of India,” Maharashtra consistently leads in onion production, contributing significantly to the national output. The state’s favorable climate, fertile soil, and advanced irrigation systems make it ideal for onion cultivation. Nashik district, in particular, is renowned for its high-quality onions, which are exported to various parts of the world.
Madhya Pradesh: In recent years, Madhya Pradesh has emerged as a significant onion-producing state, thanks to its fertile lands and supportive government policies. The state has invested in irrigation infrastructure and promoted the adoption of modern farming techniques, leading to a substantial increase in onion yields.
Karnataka: Karnataka’s diverse agro-climatic zones allow for year-round onion cultivation. The state’s farmers have embraced innovative farming practices, such as drip irrigation and fertigation, which have helped to improve water efficiency and nutrient management.
Gujarat: Gujarat’s arid and semi-arid regions are well-suited for onion cultivation. The state’s farmers have developed drought-resistant onion varieties that can thrive in water-scarce conditions. The government has also provided subsidies for drip irrigation and other water-saving technologies.
Rajasthan: Rajasthan’s sandy soils and hot climate present challenges for onion cultivation, but the state’s farmers have adapted by using innovative irrigation techniques and cultivating onion varieties that are tolerant to heat and drought.
Uttar Pradesh: Uttar Pradesh, with its vast agricultural land, has also emerged as a key onion-producing state. The state government has been promoting the cultivation of onions through various schemes and initiatives, including providing subsidies for seeds and fertilizers.
Haryana: Haryana’s strategic location and well-developed transportation network make it an important hub for onion trading and export. The state’s farmers have adopted modern farming techniques and are known for producing high-quality onions.
Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu: These southern states also contribute to the overall onion production of India. Their favorable climatic conditions support onion cultivation, making them important players in the domestic market.
Each of these states has its unique strengths and challenges when it comes to onion cultivation. Factors such as soil type, climate, irrigation facilities, and government policies all play a role in determining the productivity and profitability of onion farming in each region.
The Role of Technology and Innovation
Technology and innovation have played a crucial role in India’s success as an onion producer. Improved farming techniques, such as the use of hybrid seeds, drip irrigation, and integrated pest management, have significantly increased yields and reduced post-harvest losses.
Hybrid seeds: Hybrid onion varieties are known for their high yields, disease resistance, and uniform size and shape. These seeds have been instrumental in increasing onion production in India.
Drip irrigation: Drip irrigation is a water-efficient irrigation technique that delivers water directly to the roots of the plants, minimizing water loss through evaporation and runoff. This technique is particularly useful in arid and semi-arid regions, where water is scarce.
Integrated pest management (IPM): IPM is a holistic approach to pest control that combines various techniques, such as biological control, cultural practices, and judicious use of pesticides, to minimize the impact of pests on onion crops.
In addition to these farming techniques, advancements in storage and transportation technologies have also contributed to the growth of the onion industry. Cold storage facilities help to extend the shelf life of onions, reducing post-harvest losses and ensuring a more stable supply to the market. Improved transportation networks, including roads, railways, and ports, have made it easier to transport onions from production centers to consumption centers, both within India and abroad.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Despite its success as an onion producer, India faces several challenges in maintaining its leadership position in the global market. Climate change is a major concern, with erratic rainfall patterns and increasing temperatures potentially impacting onion yields. The lack of adequate storage facilities is also a problem, leading to significant post-harvest losses. Price volatility, influenced by factors such as weather patterns, storage facilities, and market demand, can significantly impact farmers’ incomes and consumer prices.
To address these challenges, India needs to invest in research and development to develop climate-resilient onion varieties and improve storage technologies. The government also needs to promote the adoption of sustainable agriculture practices and strengthen its infrastructure for the storage and transportation of onions.
Looking ahead, the future prospects for the Indian onion industry are bright. The country’s vast agricultural resources, coupled with its growing economy and expanding middle class, provide a strong foundation for continued growth. By addressing the challenges and capitalizing on its strengths, India can ensure that it remains the “Onion King” for years to come.
The Indian government has implemented several initiatives to support onion farmers and promote the growth of the onion industry. These initiatives include:
- Subsidies on seeds, fertilizers, and electricity
- Investments in irrigation infrastructure
- Establishment of cold storage facilities
- Promotion of sustainable agriculture practices
- Price stabilization fund
- Buffer stock scheme
These initiatives have helped to reduce the financial burden on farmers, improve yields, and stabilize prices, contributing to the overall growth of the onion industry.
Impact on Global Markets and Trade
India’s emergence as the world’s leading onion producer has had a significant impact on global markets and trade. As a major exporter of onions, India plays a crucial role in supplying this essential vegetable to countries across the globe. Its ability to maintain a consistent and reliable supply is crucial for food security in many regions, particularly in countries where onions are a staple ingredient in local cuisine.
India’s dominance in the onion market has also had an impact on international trade patterns. Countries that were previously major onion exporters, such as China and the Netherlands, have seen their market share decline as India’s exports have increased. This has led to increased competition in the global onion market, benefiting consumers by keeping prices low.
However, India’s export policies can also have a significant impact on global onion prices. When India imposes export restrictions, such as minimum export prices or export quotas, global prices tend to rise, affecting consumers in importing countries. This highlights the importance of India maintaining a stable and predictable export policy to ensure a fair and balanced global onion market.
Social and Environmental Considerations
While India’s success as an onion producer has brought economic benefits, it is also important to consider the social and environmental implications of onion cultivation. The intensive use of water for irrigation can deplete groundwater resources, particularly in arid and semi-arid regions. The overuse of chemical fertilizers and pesticides can also pollute the soil and water, harming human health and the environment.
To address these social and environmental concerns, it is important to promote the adoption of sustainable agriculture practices. This includes promoting water-efficient irrigation techniques, reducing the use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides, and implementing integrated pest management strategies.
It is also important to ensure that onion farmers receive fair prices for their produce. Price volatility can lead to financial hardship for farmers, particularly small-scale farmers who lack access to storage facilities and market information. The government needs to continue to implement policies that stabilize prices and ensure that farmers receive a fair return for their investment.
Conclusion: India’s Onion Kingdom and its Future
India’s journey to becoming the world’s leading onion producer is a testament to the country’s agricultural potential and the resilience of its farmers. By embracing technology, implementing supportive policies, and adapting to changing market conditions, India has transformed itself into the “Onion King” of the world.
However, challenges remain. Climate change, price volatility, and social and environmental concerns all pose threats to the long-term sustainability of the onion industry. To address these challenges, India needs to continue to invest in research and development, promote sustainable agriculture practices, and implement policies that support farmers and protect the environment.
Looking ahead, the future of the Indian onion industry is bright. With its vast agricultural resources, growing economy, and expanding middle class, India is well-positioned to maintain its leadership position in the global onion market for years to come. By addressing the challenges and capitalizing on its strengths, India can ensure that it remains the “Onion King” and continues to provide this essential vegetable to the world.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
What factors contributed to India becoming the world’s leading onion producer?
- Several factors have contributed to India’s rise, including improved farming techniques such as the use of hybrid seeds and drip irrigation, supportive government policies that provide subsidies and infrastructure, and favorable agro-climatic conditions across various states. “The agriculture sector in India has witnessed substantial growth in recent years, particularly in the production of staple crops and vegetables,” enabling higher yields and better quality.
-
Which states in India are the major contributors to onion production?
- Maharashtra is the largest onion-producing state in India, contributing a significant portion of the total output. Other key states include Madhya Pradesh, Karnataka, Gujarat, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, Haryana, Andhra Pradesh, and Tamil Nadu. Each state leverages unique climatic conditions and agricultural practices to support onion cultivation.
-
How does the Indian government support onion farmers?
- The Indian government provides support through various measures, including subsidies on agricultural inputs like seeds and fertilizers, investments in irrigation infrastructure, and initiatives promoting modern farming techniques. Additionally, schemes like the price stabilization fund and buffer stock schemes help mitigate price volatility, ensuring stable incomes for farmers.
-
What are the main challenges facing the Indian onion industry?
- The onion market faces several challenges, including price volatility due to fluctuating weather patterns and market demand, inadequate storage facilities leading to post-harvest losses, and the impact of climate change on crop yields. Addressing these issues requires continued investment in research, improved storage technologies, and sustainable agricultural practices.
-
How does India’s onion production impact the global market?
- As the world’s leading onion producer, India plays a critical role in supplying onions to countries worldwide. Its ability to maintain a consistent supply is crucial for global food security, especially in regions where onions are a staple. India’s export policies and market stability have significant implications for international trade and economic relations in the agricultural sector.