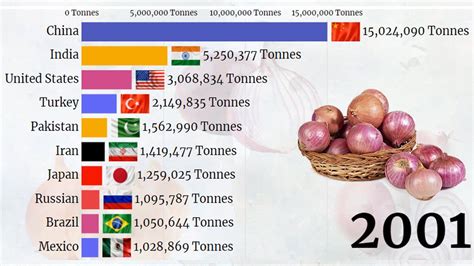
India has solidified its position as the world’s leading onion producer, contributing significantly to the global supply and domestic consumption. This dominance is driven by favorable climate conditions, agricultural practices, and government support.
India’s supremacy in onion production is underscored by its substantial share of the global market. “India is the largest exporter of onions,” as noted by agricultural experts, highlighting the country’s pivotal role in meeting international demand. The nation’s extensive agricultural infrastructure and dedicated farming communities contribute to this impressive output. However, this success is not without its challenges, including price volatility, storage limitations, and export restrictions, which can impact both farmers and consumers. This article delves into the factors behind India’s leading role, the challenges it faces, and the broader implications for the global onion market.
Factors Contributing to India’s Onion Production Prowess
Several key elements contribute to India’s dominance in onion production.
-
Favorable Climate and Soil Conditions: India’s diverse agro-climatic zones provide ideal conditions for onion cultivation. The availability of both Rabi (winter-sown) and Kharif (monsoon-sown) seasons allows for year-round production in different regions. The fertile soil in states like Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Karnataka, and Gujarat further supports high yields.
-
Advanced Agricultural Practices: Indian farmers have increasingly adopted modern agricultural techniques, including improved irrigation methods, high-yielding seed varieties, and effective pest management strategies. The use of drip irrigation and fertigation has significantly enhanced water use efficiency and nutrient delivery, leading to higher productivity.
-
Government Support and Policies: The Indian government has implemented various initiatives to support onion farmers, including subsidies for inputs such as seeds, fertilizers, and pesticides. Market intervention schemes, such as the Price Stabilization Fund (PSF), aim to stabilize onion prices and protect farmers from distress sales during periods of oversupply.
-
Extensive Agricultural Infrastructure: India has a well-established agricultural infrastructure, including a network of agricultural research institutions, extension services, and marketing boards. These institutions provide farmers with access to the latest technologies, best practices, and market information, enabling them to optimize their production and marketing strategies.
-
Dedicated Farming Communities: Onion farming is a labor-intensive activity, and India benefits from a large pool of dedicated and experienced farmers who have honed their skills over generations. These farmers possess invaluable knowledge of local conditions and traditional farming practices, which contribute to the quality and quantity of onion production.
Regional Production Hubs
India’s onion production is concentrated in a few key states, each contributing significantly to the national output.
-
Maharashtra: Maharashtra is the largest onion-producing state in India, accounting for a significant share of the country’s total production. The Nashik district in Maharashtra is particularly renowned for its high-quality onions.
-
Madhya Pradesh: Madhya Pradesh has emerged as a major onion-producing state in recent years, benefiting from favorable climate conditions and government support. The state has witnessed a significant increase in onion production, contributing to the overall growth of the sector.
-
Karnataka: Karnataka is another important onion-producing state in South India. The state’s favorable climate and irrigation facilities support onion cultivation throughout the year.
-
Gujarat: Gujarat is known for its onion varieties that are suitable for export. The state’s proximity to major ports and export markets facilitates the trade of onions to other countries.
Challenges in Onion Production and Supply Chain
Despite its leading position, India’s onion sector faces several challenges that need to be addressed to ensure sustainable growth and stability.
-
Price Volatility: Onion prices are highly volatile in India, fluctuating widely due to seasonal factors, weather conditions, and market dynamics. This price volatility can create uncertainty for farmers and consumers, leading to distress sales and food inflation.
-
Storage Limitations: Onions are perishable commodities with a limited shelf life, particularly during the monsoon season. Inadequate storage facilities and post-harvest losses result in significant wastage, further exacerbating price volatility.
-
Export Restrictions: The Indian government often imposes export restrictions on onions to control domestic prices and ensure adequate supply for local consumption. These restrictions can disrupt international trade and affect the livelihoods of onion farmers who rely on export markets.
-
Infrastructure Deficiencies: Poor infrastructure, including inadequate transportation, cold storage, and processing facilities, hinders the efficient movement of onions from production areas to consumption centers and export markets. This can lead to delays, spoilage, and higher transaction costs.
-
Climate Change Impacts: Climate change poses a growing threat to onion production in India, with erratic rainfall, prolonged droughts, and extreme temperatures affecting yields and quality. Farmers need to adopt climate-resilient agricultural practices to mitigate these impacts.
Government Initiatives to Support Onion Production
The Indian government has implemented several initiatives to address the challenges faced by the onion sector and promote sustainable growth.
-
Price Stabilization Fund (PSF): The PSF aims to stabilize onion prices by procuring onions during periods of surplus production and releasing them in the market during periods of shortage. This helps to protect farmers from distress sales and ensure a stable supply of onions for consumers.
-
Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH): The MIDH provides financial assistance to farmers for various activities related to onion production, including the adoption of improved technologies, the construction of storage facilities, and the promotion of post-harvest management practices.
-
Agricultural Infrastructure Development: The government is investing in the development of agricultural infrastructure, including cold storage facilities, pack houses, and transportation networks, to reduce post-harvest losses and improve the efficiency of the supply chain.
-
Promotion of Export-Oriented Production: The government is promoting the production of onion varieties that are suitable for export and providing incentives to exporters to boost onion exports.
-
Research and Development: The government supports research and development efforts to develop high-yielding, disease-resistant onion varieties and improve agronomic practices.
Impact on the Global Onion Market
India’s dominance in onion production has a significant impact on the global onion market.
-
Price Influence: India’s onion production and export policies can influence global onion prices. Export restrictions or supply disruptions in India can lead to price spikes in international markets.
-
Competition: India competes with other major onion-producing countries, such as China, Egypt, and the Netherlands, in the global market. The competitiveness of Indian onions depends on factors such as price, quality, and availability.
-
Market Access: India’s access to key export markets depends on trade agreements and sanitary and phytosanitary regulations. The government is working to negotiate favorable trade terms and ensure compliance with international standards.
-
Supply Chain Integration: The integration of Indian onions into the global supply chain requires efficient logistics, transportation, and quality control measures. The government is promoting the development of integrated value chains to enhance the competitiveness of Indian onions in the global market.
Future Prospects
The future of India’s onion sector looks promising, with significant potential for growth and development.
-
Increased Production: With continued investment in research and development, improved agricultural practices, and supportive government policies, India can further increase its onion production to meet growing domestic and international demand.
-
Improved Storage and Processing: The development of modern storage and processing facilities can reduce post-harvest losses and add value to onions, enhancing their shelf life and marketability.
-
Diversification of Export Markets: Diversifying export markets and reducing reliance on a few key destinations can mitigate the impact of trade restrictions and ensure stable export earnings.
-
Climate Resilience: Adopting climate-resilient agricultural practices, such as drought-resistant varieties and water-efficient irrigation methods, can help to ensure the sustainability of onion production in the face of climate change.
-
Farmer Empowerment: Empowering onion farmers through access to information, technology, and market opportunities can improve their livelihoods and promote sustainable agricultural practices.
Economic Significance
The onion sector holds substantial economic significance for India, impacting various aspects of the nation’s economy.
-
Contribution to GDP: Onion production contributes a noteworthy share to India’s agricultural GDP. The cultivation, processing, and trade of onions generate substantial economic activity, supporting livelihoods across the country.
-
Employment Generation: The onion sector is a significant source of employment, particularly in rural areas. Onion farming, harvesting, sorting, packaging, and transportation create employment opportunities for millions of people.
-
Export Earnings: India is a major exporter of onions, earning valuable foreign exchange. Onion exports contribute to the country’s trade balance and help to finance imports.
-
Rural Development: Onion production plays a crucial role in rural development by providing income and employment opportunities to farmers and agricultural laborers in rural areas.
-
Food Security: Onions are an essential part of the Indian diet, and domestic production is critical for ensuring food security and affordability for consumers.
Technological Advancements
The adoption of technology is transforming the onion sector in India, improving productivity, efficiency, and sustainability.
-
Precision Farming: Precision farming techniques, such as GPS-based soil mapping, variable rate irrigation, and drone-based crop monitoring, are helping farmers to optimize inputs and improve yields.
-
Improved Irrigation Systems: Drip irrigation and fertigation systems are enhancing water use efficiency and nutrient delivery, reducing water wastage and improving onion quality.
-
Post-Harvest Management Technologies: Advanced post-harvest management technologies, such as controlled atmosphere storage and modified atmosphere packaging, are extending the shelf life of onions and reducing post-harvest losses.
-
Digital Platforms: Digital platforms are providing farmers with access to market information, weather forecasts, and expert advice, enabling them to make informed decisions and improve their farming practices.
-
Mechanization: Mechanization of onion farming operations, such as planting, harvesting, and sorting, is reducing labor costs and improving efficiency.
Sustainability Initiatives
Promoting sustainability in the onion sector is essential for ensuring long-term productivity and environmental protection.
-
Integrated Pest Management (IPM): IPM practices are reducing the use of chemical pesticides and promoting the use of bio-control agents, minimizing the environmental impact of onion production.
-
Water Conservation: Water conservation techniques, such as drip irrigation, rainwater harvesting, and soil moisture management, are reducing water consumption and improving water use efficiency.
-
Soil Health Management: Soil health management practices, such as crop rotation, organic farming, and conservation tillage, are improving soil fertility and reducing soil erosion.
-
Waste Management: Waste management practices, such as composting and vermicomposting, are converting onion waste into valuable organic fertilizers, reducing environmental pollution.
-
Renewable Energy: The use of renewable energy sources, such as solar power, for irrigation and post-harvest processing is reducing the carbon footprint of onion production.
Global Trade Dynamics
The global onion trade is influenced by various factors, including production levels, demand patterns, trade policies, and transportation costs.
-
Major Exporters: India, China, the Netherlands, Egypt, and Mexico are the major exporters of onions in the global market.
-
Major Importers: The United States, Malaysia, the United Kingdom, Germany, and the United Arab Emirates are the major importers of onions.
-
Trade Agreements: Trade agreements, such as free trade agreements and preferential trade agreements, can influence the flow of onion trade between countries.
-
Transportation Costs: Transportation costs play a significant role in determining the competitiveness of onions in the global market.
-
Sanitary and Phytosanitary Regulations: Sanitary and phytosanitary regulations can restrict the import of onions from countries that do not meet the required standards.
Conclusion
India’s position as the world’s top onion producer is a testament to its agricultural capabilities, favorable climate, and the dedication of its farming communities. While challenges such as price volatility and storage limitations exist, ongoing government initiatives and technological advancements offer promising solutions. The country’s role in the global onion market is significant, influencing prices and supply chains worldwide. By focusing on sustainable practices, improved infrastructure, and farmer empowerment, India can further strengthen its position and ensure the long-term viability of its onion sector. As India continues to refine its agricultural practices and address existing challenges, its dominance in onion production is expected to remain secure, continuing to feed both its population and the world.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
What makes India the largest onion producer in the world? India’s favorable climate, fertile soil, advanced agricultural practices, government support, and extensive agricultural infrastructure contribute to its leading position in onion production. As quoted from agricultural experts, “India is the largest exporter of onions,” highlighting its pivotal role. The diverse agro-climatic zones allow year-round production, particularly in states like Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Karnataka, and Gujarat.
-
What are the main challenges faced by the onion sector in India? The onion sector faces several challenges, including price volatility, storage limitations, export restrictions, infrastructure deficiencies, and the impacts of climate change. Price volatility can lead to uncertainty for farmers and consumers. Inadequate storage facilities cause significant wastage, and export restrictions can disrupt international trade.
-
What initiatives has the Indian government implemented to support onion farmers? The Indian government has implemented various initiatives, including the Price Stabilization Fund (PSF), which aims to stabilize onion prices by procuring onions during periods of surplus and releasing them during shortages. The Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH) provides financial assistance for activities related to onion production, and the government invests in agricultural infrastructure development.
-
How does India’s onion production influence the global market? India’s onion production and export policies can significantly influence global onion prices. Export restrictions or supply disruptions in India can lead to price spikes in international markets. India competes with other major onion-producing countries and its access to key export markets depends on trade agreements.
-
What are the future prospects for the onion sector in India? The future of India’s onion sector is promising, with potential for increased production, improved storage and processing facilities, diversification of export markets, climate resilience, and farmer empowerment. Continued investment in research and development, improved agricultural practices, and supportive government policies will drive further growth and development.









